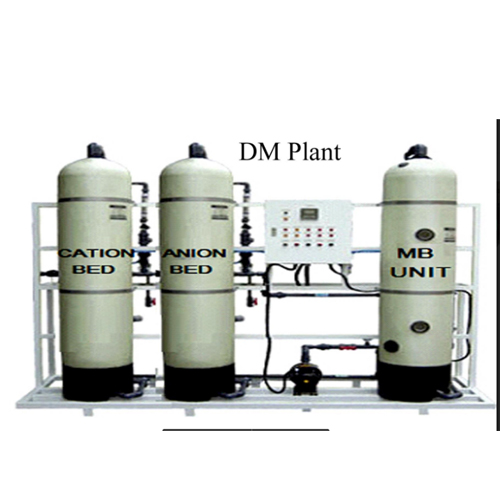
A DM (Demineralization) plant with a capacity of 1000 liters per day (LPD) is a crucial system used in various industries to remove minerals and salts from water, producing high-quality demineralized water. Typically, such plants employ ion exchange processes, utilizing ion exchange resins to remove ions such as calcium, magnesium, and sodium from the water.
With a capacity of 1000 LPD, this DM plant can cater to the demineralization needs of small to medium-scale industrial processes or laboratories. It involves several key components such as resin tanks, regeneration systems, filters, pumps, and monitoring instruments.
The functioning of the DM plant involves passing raw water through various stages where ion exchange resins selectively remove ions, resulting in demineralized water. Regeneration of exhausted resins is an integral part of the process, ensuring continuous operation and efficiency of the plant.
Proper maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure the longevity and performance of the DM plant. Regular regeneration of ion exchange resins, monitoring of water quality parameters, and timely replacement of consumables are necessary to maintain optimal performance.